Images, triggers, causes, breaks, and remedies: An overview of battles' indicators, causes, warnings of fractures, and suggested treatments.
Basilar skull fractures are a serious injury that typically results from high-impact trauma, such as motor vehicle accidents, falls, or blunt force injuries to the head. These fractures occur at the base of the skull and can lead to a range of symptoms and complications.
One of the most notable signs of a basilar skull fracture is Battle's sign, a crescent-shaped bruise that appears behind one or both ears. This bruising is not a result of direct injury but is caused by blood pooling due to a broken bone in the skull. Its presence warrants urgent investigation for a skull base fracture and associated complications like cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks and intracranial injury.
In addition to Battle's sign, other symptoms of basilar skull fractures include bruising around the eyes (raccoon eyes), clear fluid leaking from the nose or ears (CSF), headache, localized pain, and swelling, hearing loss or ringing in the ear, vomiting, confusion, or loss of consciousness, and possible cranial nerve involvement leading to symptoms like double vision.
The complications of basilar skull fractures can be severe. Intracranial bleeding, such as epidural or subdural hematomas causing brain compression, is a significant risk. Traumatic brain injury (TBI) from associated brain tissue damage is also possible. CSF leaks increase the risk of infections like meningitis, which can be life-threatening, especially in those with basilar skull fractures. Post-traumatic seizures and cranial nerve palsies are also potential complications.
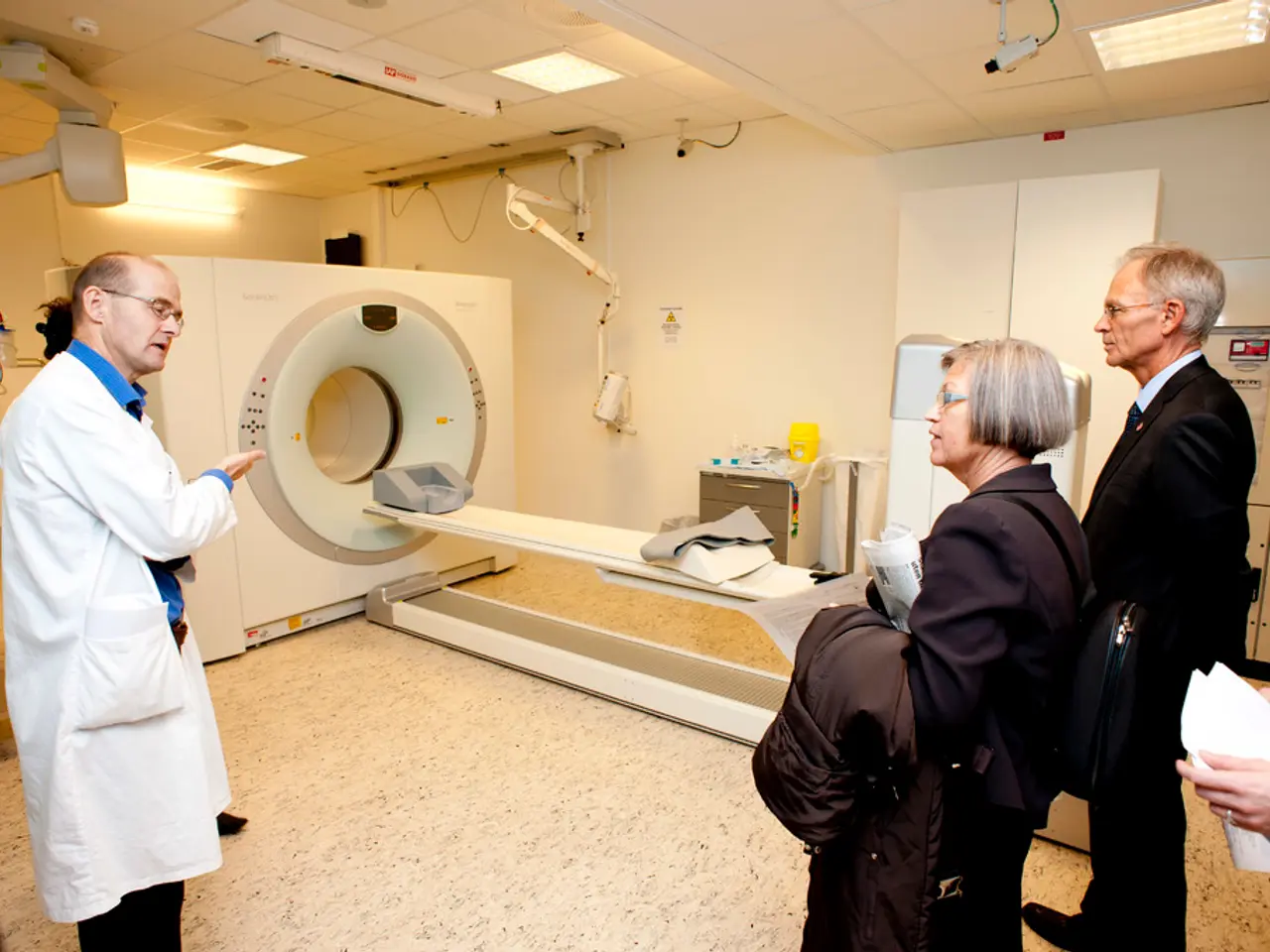
Early diagnosis and appropriate management are crucial in preventing long-term neurological damage and other sequelae. Immediate medical evaluation with imaging (CT scans) is necessary to assess fracture severity and brain injury. Treatment may involve conservative management or surgical intervention for hematoma evacuation, dural tear repair, bone fracture repair, antibiotics to prevent or treat infections, seizure medication, and supportive care for neurological deficits and rehabilitation for long-term effects.
Given the potential severity of basilar skull fractures and associated complications, it is essential to seek emergency care after a head injury. Even if no visible bruise is present, any signs of meningitis symptoms, such as fever, stiff neck, headache, confusion, sensitivity to light, nausea or vomiting, loss of consciousness, or vision changes, warrant immediate medical attention.
Proper helmets, seatbelts, and protective equipment can help reduce the risk of skull fractures caused by physical violence, contact sports, car accidents, motorcycle accidents, bicycle accidents without a helmet, and falls. By understanding the signs and potential complications of basilar skull fractures, individuals can take steps to minimise their risk and seek prompt medical attention if necessary.
- Obesity, a common health-and-wellness issue, can exacerbate the risk of accidents and falls, potentially leading to basilar skull fractures.
- Scientific studies have shown a predictive relationship between basilar skull fractures and certain medical conditions, such as depression or bipolar disorders, due to the trauma's psychological impact.
- In addition to physical symptoms, basilar skull fractures can also lead to neurological disorders, like PSA (pseudotumor cerebri) or traumatic brain injury, causing changes in brain function.
- An AD (advertisement) campaign highlighting safety precautions could remind people to wear helmets and seatbelts, thus reducing the risk of accidentsandfalls and associated basilar skull fractures.
- In the event of an accident causing a basilar skull fracture, the individual may experience symptoms like asymmetrical facial paralysis (respectively Bell's palsy or cranial nerve involvement), which require immediate medical attention.
- AQ (Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America) advocates for public awareness of health-related issues, including the increased risk of asthma due to fine particles produced during a motor vehicle accident or other incidents leading to basilar skull fractures.
- In the long run, neglected basilar skull fractures can cause complications such as chronic mental health issues, like depression, and long-term neurological disorders, as the injury may affect the brain's structure and function.
- Meningitis, a life-threatening infection, is an additional risk that can follow a basilar skull fracture due to CSF leakage, highlighting the need for prompt medical intervention in treating these severe medical conditions.