Normal Salivary Gland Biopsy: A Relief for Patients, a Valuable Diagnostic Tool
A recent normal biopsy result has shown healthy tissue in the salivary glands, with no signs of disease or abnormal growths. This news comes as a relief, as salivary gland tumors, while often benign, can also be malignant. Let's delve into the details and understand the role of salivary gland biopsies in diagnosing various conditions.
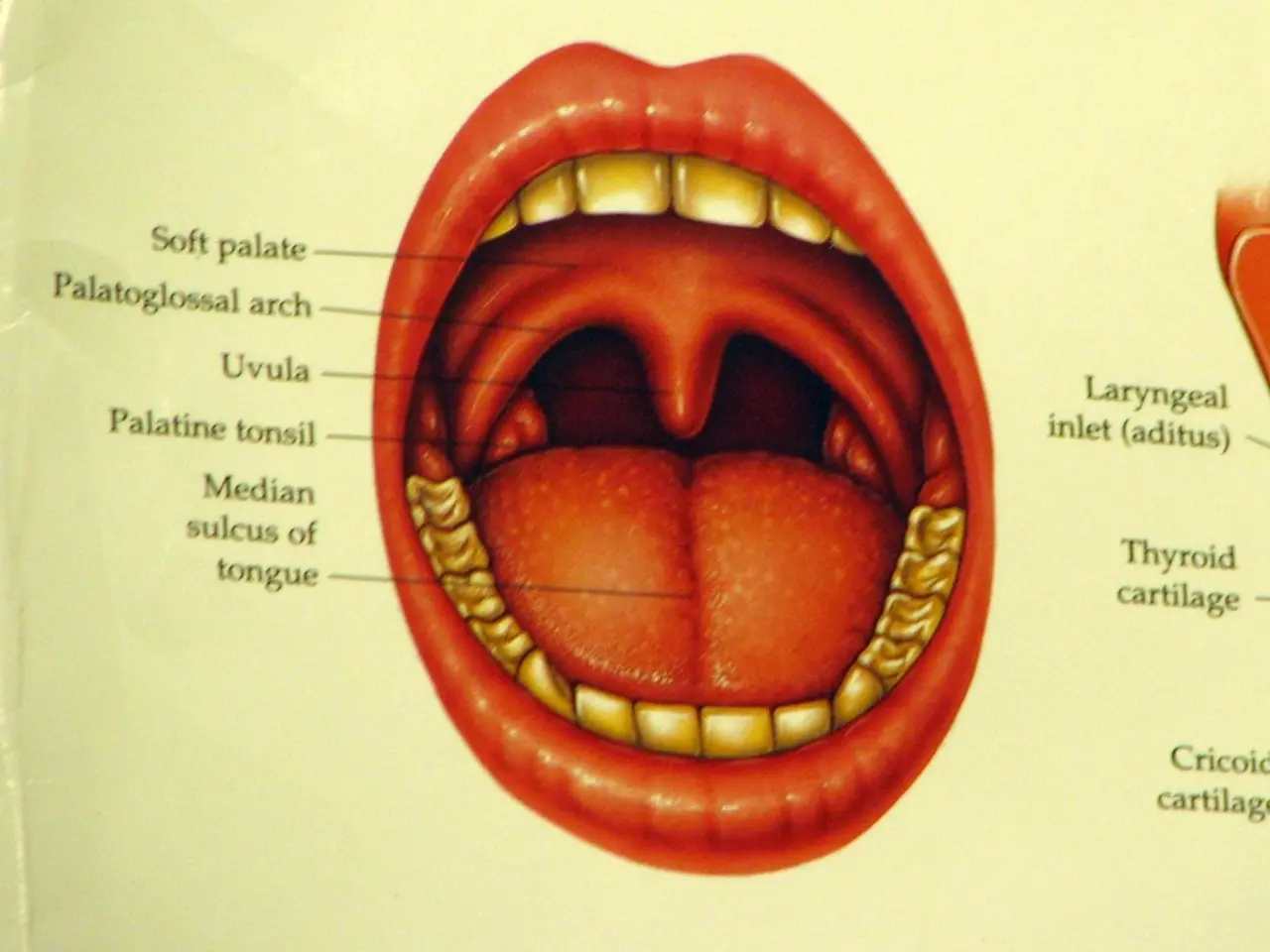
Salivary glands, located beneath the tongue and over the jawbone near the ear, play a crucial role in digestion and oral health by secreting saliva. The main glands include the parotid, sublingual, and submandibular glands. When abnormalities occur, a salivary gland biopsy may be recommended to examine any lumps, swelling, or blockages.
The biopsy, typically performed in a doctor's office using a needle aspiration technique, involves removing cells or tissue for laboratory examination. It can help diagnose conditions such as salivary gland infections, cancer, or sarcoidosis. In some cases, it may also aid in confirming the presence of the chronic autoimmune disorder, Sjögren syndrome, by showing lymphocytic infiltrates or other histopathologic changes in the sample. This information is vital for selecting the appropriate treatment strategy.
Preparation for the biopsy may involve fasting and stopping blood-thinning medications. While the biopsy itself is not a treatment, it serves as a powerful diagnostic tool, enabling healthcare professionals to tailor treatments to the specific condition. For instance, treatments for Sjögren syndrome focus on symptom relief and improving overall well-being, such as using artificial tears or medications to boost saliva production.
In conclusion, a normal salivary gland biopsy result indicates healthy tissue, providing reassurance and guiding healthcare professionals in managing any related conditions. As a valuable diagnostic tool, the biopsy helps in understanding and treating various salivary gland disorders, from infections to autoimmune diseases like Sjögren syndrome.